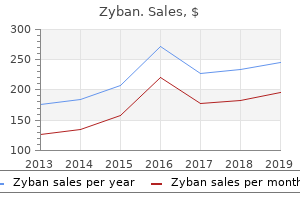
"Cheap zyban 150mg without a prescription, anxiety 9 months after baby".
By: B. Kayor, M.S., Ph.D.
Assistant Professor, Liberty University College of Osteopathic Medicine (LUCOM)
Branchial cartilage and cervical auricle can be present at the site of external orifice of the branchial fistula depression nursing definition discount zyban uk. Cystic Hygroma Aetiology At about the sixth week of intrauterine life depression symptoms recurring purchase generic zyban canada, primitive lymph sacs develop in the mesoblasts. The principal pair is situated in the neck between the jugular and subclavian veins, and corresponds to the lymph hearts of the lower animals. Sequestration of lymphatic tissue consequent upon failure of an important tributary of the primitive lymphatic system to link up with other lymphatic vessels or with the venous system accounts for the appearance of these swellings. Cystic hygroma, like sternomastoid tumour, is earliest to appear, usually during early infancy or may be present at birth. Site It occupies the lower-third of the neck and passes upwards towards the ear as it enlarges. Due to its many compartments and their intercommunications, the swelling is softly cystic and partially compressible but it is brilliantly translucent. It often extends downwards behind the clavicle to lie upon the dome of pleura, sometimes into the axilla or may occur in the groin or mediastinum. Pathology It consists of an aggregation of cysts, like a mass of soap bubbles, the larger cysts are near the surface while smaller ones lie deeply and tend to infiltrate the muscle planes. Each cyst is lined by a single layer of endothelium, having the appearance of mosaic and is filled with clear lymph. Clinical Course During infancy its behaviour is uncertain, it may grow rapidly and obstruct respiration and aspiration of the contents may be required. Treatment Complete dissection of the cyst at an early age is the treatment of election. If the cyst is removed incompletely, there is a danger of dehydration because of lymph leakage, unless the fluid balance is maintained. It is a single cyst filled with lymph and is usually found in the supraclavicular triangle. Sternomastoid Tumour this usually occurs as hard, fusiform swelling of the lowerthird of the sternomastoid at 1-2 weeks of birth. It remains stationary in size up to 3 months, then disappears gradually but if not treated may cause congenital torticollis. If still untreated, facial asymmetry ensues and the face and cranium on the affected side fail to lengthen pari passu with the normal side. Manipulation: It is done after the tumour disappears, by two persons, one hold the shoulders and other extends the neck towards the nonaffected side. Through a transverse incision the swelling and muscle in the neighbourhood is excised without injuring the eleventh nerve. No attempt is made to close the gap, but subcutaneous tissues are approximated accurately before closing the wound. It usually contains the jugulo-omohyoid nodes and may contain jugulodiagastric node. Level 4: Lower jugular group this consists of lymph nodes located around middle third of internal jugular vein extending from cricoid cartilage down to clavicle inferiorly. Level 5: Post-triangle group these nodes are located along the lower half of spinal accessory nerve. The transverse cervical artery supraclavicular nodes are also included in this group. The posterior border is the anterior border of trapezius and anterior boundary is the posterior border of the sternomastoid muscle. Level 6: Anterior compartment group (visceral group) this consists of the lymph nodes surrounding the midline visceral structures of neck extending from hyoid bone superiorly to suprasternal notch inferiorly. It contains parathyroid, the paratracheal, perilaryngeal and prelaryngeal lymph nodes. Level 2: Upper jugular group this consists of lymph nodes located around upper third of internal jugular vein and adjacent spinal accessory nerve extending from skull base down to level of carotid bifurcation where digastric muscle crosses the jugular vein. Level 3: Middle jugular group this consists of lymph nodes located around middle third of internal jugular vein extending from carotid bifurcation superiorly down to .
Subsequently mood disorder kids purchase 150 mg zyban, the secondary spermatocytes undergo a second meiotic division to form four haploid spermatids depression and alcohol generic zyban 150 mg otc, which are approximately half the size of secondary spermatocytes. The spermatids are gradually transformed into four mature sperm by a process known as spermiogenesis. The entire process of spermatogenesis, which includes spermiogenesis, takes approximately 2 months. When spermiogenesis is complete, the sperms enter the lumina of the seminiferous tubules. Sertoli cells lining the seminiferous tubules support and nurture the germ cells and may be involved in the regulation of spermatogenesis. Sperms are transported passively from the seminiferous tubules to the epididymis, where they are stored and become functionally mature. The epididymis is the elongated coiled duct along the posterior border of the testis (see. It is continuous with the ductus deferens (vas deferens), which transports the sperms to the urethra. The head, composed mostly of the nucleus, is partly covered by the caplike acrosome, an organelle containing enzymes. The tail of the sperm consists of three regions: the middle piece, principal piece, and end piece. C, A human secondary oocyte (Г-200), surrounded by the zone pellucida and corona radiata. The head of the sperm forms most of the bulk of the sperm and contains the haploid nucleus. The anterior two thirds of the nucleus is covered by the acrosome, a caplike saccular organelle containing several enzymes. When released, these enzymes facilitate dispersion of the follicular cells of the corona radiata and sperm penetration of the zona pellucida during fertilization. The tail of the sperm consists of three segments: middle piece, principal piece, and end piece (see. The tail provides the motility of the sperm that assists its transport to the site of fertilization. The middle piece of the tail contains mitochondria, which provide the adenosine triphosphate necessary for activity. For example, recent studies indicate that proteins of the Bcl-2 family are involved in the maturation of germ cells, as well as their survival at different stages. For normal spermatogenesis, the Y chromosome is essential; microdeletions result in defective spermatogenesis and infertility. Oogenesis continues to menopause, which is permanent cessation of the menses (bleeding associated with the menstrual cycles). Prenatal Maturation of Oocytes During early fetal life, oogonia proliferate by mitosis. Oogonia enlarge to form primary oocytes before birth; for this reason, no oogonia are shown in Figures 2-1 and 2-3. As a primary oocyte forms, connective tissue cells surround it and form a single layer of flattened, follicular epithelial cells (see. The primary oocyte enclosed by this layer of cells constitutes a primordial follicle (see. As the primary oocyte enlarges during puberty, the follicular epithelial cells become cuboidal in shape and then columnar, forming a primary follicle (see. The primary oocyte soon becomes surrounded by a covering of amorphous acellular glycoprotein material, the zona pellucida. Scanning electron microscopy of the surface of the zona pellucida reveals a regular meshlike appearance with intricate fenestrations. Primary oocytes begin the first meiotic division before birth, but completion of prophase does not occur until adolescence. The follicular cells surrounding the primary oocyte are believed to secrete a substance, oocyte maturation inhibitor, which keeps the meiotic process of the oocyte arrested. Postnatal Maturation of Oocytes Beginning during puberty, usually one follicle matures each month and ovulation occurs, except when oral contraceptives are used. The long duration of the first meiotic division (up to 45 years) may account in part for the relatively high frequency of meiotic errors, such as nondisjunction (failure of paired chromatids to dissociate), that occur with increasing maternal age.
When time is limited for dental care before the oncological therapy starts depression dsm code order discount zyban on-line, infections depression what to do zyban 150 mg low price, extractions, periodontal care, and sources of irritation should be given higher treatment priority than carious teeth, root canal therapy for permanent teeth, and replace ment of faulty restorations. The risk for pulpal infection and pain should determine which carious lesions are to be treated first, because a pulpal infection during immuno suppression could lead to a life-threatening situation. In cases of emergency, the physician must be contacted before any dental treatment is initiated, because platelet transfusions, antibiotic coverage beyond endocardi this prevention, and hospital admission may be necessary for dental management. When there is time before the initiation of cancer therapy, dental scaling and prophylaxis should be done, defective restorations should be repaired, and teeth with sharp edges should be polished. Although there have been no studies to date that address the safety of performing pulp therapy in primary teeth before the initiation of che motherapy and/or radiotherapy, it is prudent to provide a more radical treatment in the form of extraction to mini mize the risk for oral and systemic complications of failed pulp therapy during immunosuppression periods, which can have a significant impact on cancer treatment. Symptom atic nonvital permanent teeth should receive root canal therapy at least 1 week before initiation of cancer therapy. Fixed orthodontic appliances and space maintainers should be removed if the patient has poor oral hygiene or the treatment protocol carries a risk for the development of moderate to severe mucositis. This precaution does not apply to smooth appliances such as band and loops and fixed lower lingual arches. Removable appli ances and retainers that fit well may be worn as long as toler ated by the patient who shows good oral care. If band removal is not possible, mouth guards or orthodontic wax should be used to decrease tissue trauma. If the patient cannot comply with this recommendation, loose teeth should be removed. Impacted teeth, root tips, partially erupted third molars, teeth with periodontal pockets greater than 6 mm, teeth with acute infections, and nonrestorable teeth should be removed at least 4 to 7 days (ideally 2 weeks) before cancer therapy starts to allow adequate healing? Antibiotics should be given for 7 to 10 days after ward, with the extraction subsequently done when the patienfs hematologic status allows it. When the patient is in the maintenance phase of the treat ment and the overall prognosis is good, it is likely that the hematologic status is close to normal. Orthodontic treatment may start or resume after completion of all therapy and after at least a 2-year disease-free sur vival. However, the clinician must assess any dental developmental disturbances caused by the cancer therapy, especially in chil dren treated before the age of 6 years (Figure 4 8). However, specific guidelines for orthodontic management, including optimal force and pace, remain undefined. The role of growth hormone in the development of the craniofacial structures in pediatric cancer patients has not been fully established. Pediatric patients with cancer may develop osteoporosis, and many receive bisphosphonates, which leads to additional concerns in the delivery of oral and dental care. Orthodontic treatment consid erations are the same as discussed in the previous section. Evidence of engraft ment is usually evident between days 20 and 30, sometimes earlier, by increased peripheral white cell and platelet counts; it is substantiated by the presence of donor cells on marrow aspirations. The occur rence and severity of mucositis show great individual vari ability, with tissue changes noticeable between 4 and 7 days after the initiation of therapy and generally lasting from 10 to 14 days/4. Muco sitis and all other acute and long-term complications of che motherapy and radiotherapy have been extensively reviewed elsewhere. Section on Hematology/Oncology Committee on Genetics, American Health supervision for children with sickle cell Pediatrics 109(3):526-535, 2002. National Institutes of Health, National Heart, Lung, and Blood Institute Division of Blood Diseases and Resources: the management ofsickle cell disease, ed 4. Briek C: Herpesvirus-induced diseases: oral manifestations and current treatment options, J Cal Dent Assoc 28(12):91 1-921, 2000. Hou G-L, Huang J-S, Tsai C-C: Analysis of oral manifestations of leukemia: a retrospective study, Oral Dis 3 (1):31-38, 1997. Gaziev J, Lucarelli G: Stem cell transplantation for hemoglobinopathies, Curr Opin Peditrtr 1 5 (1):24-3 1. C, Freemau K et al: Outcomes of placing dental implants in patients taking oral bisphosphonates: a review of 1 15 cases. Zahrowski calling for a proactive approach, Am] Orthod Dentof acial Orthop 1 3 1 (3):3 1 1-320, 2007. American Academy of Pediatrics, Committee on Substance Abuse and Committee on Children with Disabilities: Fetal alcohol syndrome and alcohol-related neurodevelopmental disorders, Pediatrics 1 06(2 pt 0:358-3 6 1, 2000. Giangrande P: Oral care f people with hemophilia or or a hereditary bleeding tet1dency.
This increase is small mood disorder diagnosis buy zyban now, about 2 mm on the average anxiety xr buy 150 mg zyban overnight delivery, but it does contribute to resolution of early crowding of the incisors. More width is gained in the maxillary arch than in the mandibular, and more is gained by boys than girls. For this reason, girls have a greater liability to incisor crowding, particularly mandibular incisor crowding. As the permanent incisors replace them, these teeth lean slightly forward, which arranges them along the arc of a larger circle. Although this change is also small, it contributes 1 to 2 mm of additional space in the average child. As the permanent incisors erupt, the canine teeth not only widen out slightly but move slightly back into the primate space. The additional space to align mandibular incisors, after the period of mild normal crowding, is derived from three sources: (1) a slight increase in arch width across the canines, (2) slight labial positioning of the central and lateral incisors, and (3) a distal shift of the permanent canines when the primary first molars are exfoliated. The primary molars are significantly larger than the premolars that replace them, and the "leeway space" provided by this difference offers an excellent opportunity for natural or orthodontic adjustment of occlusal relationships at the end of the dental transition. Both arch length (L), the distance from a line perpendicular to the mesial surface of the permanent first molars to the central incisors, and arch circumference (C) tend to decrease during the transition. Since the primate space in the maxillary arch is mesial to the canine, there is little opportunity for a similar change in the anteroposterior position of the maxillary canine. It is important to note that all three of these changes occur without significant skeletal growth in the front of the jaws. The slight increases in arch dimension during normal development are not sufficient to overcome discrepancies of any magnitude, so crowding is likely to persist into the permanent dentition if it was severe initially. The mandibular permanent central incisors are almost always in proximal contact from the time that they erupt. In the maxillary arch, however, there may continue to be a space, called a diastema, between the maxillary permanent central incisors. A central diastema tends to close as the lateral incisors erupt but may persist even after the lateral incisors have erupted, particularly if the primary canines have been lost or if the upper incisors are flared to the labial. This is another of the variations in the normal developmental pattern that occur frequently enough to be almost normal. The position of the incisors tends to improve when the permanent canines erupt, but this condition increases the possibility that the canines will become impacted. Since the flared and spaced upper incisors are not very esthetic, this is referred to as the "ugly duckling stage" of development (Figure 3-33). The greater the amount of spacing, the less the likelihood that a maxillary central diastema will totally close on its own. As a general guideline, a maxillary central diastema of 2 mm or less will probably close spontaneously, while total closure of a diastema initially greater than 2 mm is unlikely. Space Relationships in Replacement of Canines and Primary Molars In contrast to the anterior teeth, the permanent premolars are smaller than the primary teeth they replace (Figure 3-34). The mandibular primary second molar is on the average 2 mm larger than the second premolar, while in the maxillary arch, the primary second molar is 1. The primary first molar is only slightly larger than the first premolar but does contribute an extra 0. When the second primary molars are lost, the first permanent molars move forward (mesially) relatively rapidly, into the leeway space. This decreases both arch length and arch circumference, which are related but not the same thing, and are commonly confused (see Figure 3-32). Even if incisor crowding is present, the leeway space is normally taken up by mesial movement of the permanent molars. The flush terminal plane relationship, shown in the middle left, is the normal relationship in the primary dentition. When the first permanent molars erupt, their relationship is determined by that of the primary molars. The molar relationship tends to shift at the time the second primary molars are lost and the adolescent growth spurt occurs, as shown by the arrows. The amount of differential mandibular growth and molar shift into the leeway space determines the molar relationship, as shown by the arrows as the permanent dentition is completed.
Contoh: Diagnosis Utama Diagnosis Sekunder: Hematuria: Varises vena tungkai Papilomata dinding belakang kandung kemih Pengobatan Spesialisasi Dikode Papilomata: Eksisi diatermi papillomata: Urologi dinding belakang kandung kemih Hematuria dan Varises (D41 anxiety 30001 buy zyban 150 mg with visa. Penyakit jantung iskemik dan Otosklerosis sebagai diagnosis sekunder Contoh: Diagnosis Utama Diagnosis Sekunder Tidak ada informasi terapi Dikode Kejang demam (R56 depression glass test cheap 150 mg zyban free shipping. Jika diagnosis yang tercatat sebagai diagnosis utama menguraikan suatu kondisi secara umum, sedangkan suatu istilah yang bisa memberikan informasi yang lebih tepat mengenai tempat atau bentuk kondisi tersebut tercatat sebagai diagnosis sekunder, maka pilihlah yang diagnosis sekunder tersebut sebagai diagnosis utama. Contoh: Diagnosis Utama Diagnosis Sekunder: Cerebrovascular accident: Diabetes mellitus Hipertensi Perdarahan otak Dikode Perdarahan otak (I61. Jika suatu gejala atau tanda dicatat sebagai diagnosis utama dan disebabkan oleh suatu kondisi atau diagnosis sekunder, maka pilihlah gejala tersebut sebagai diagnosis utama. Jika dua kondisi atau lebih tercatat sebagai pilihan diagnostik untuk diagnosis utama, pilihlah kondisi pertama yang tercatat. Contoh: Diagnosis Utama: Sakit:kepala karena stress atau tegangan otot atau sinusitis akut Diagnosis Sekunder Sakit kepala sebagai diagnosis utama dikode R51. Contoh: Diagnosis Utama akut Diagnosis Sekunder:Kholesistitis akut sebagai diagnosis utama dikode K81. Petunjuk untuk bab-bab spesifik Berikut ini adalah beberapa petunjuk untuk bab-bab spesifik dimana masalah mungkin timbul pada saat memilih kode diagnosis utama. Pedoman dan Rule umum berlaku untuk:Infectious gastroenteritis sebagai diagnosis utama dikode: Gastroenteritis akibat infeksi atau: Kholesistitis akut atau pankreatitis -40- semua bab kecuali jika dalam petunjuk untuk babbab spesifik dibawah ini menyatakan lain. Kondisi-kondisi yang bisa diklasifikasikan pada dua subkategori atau lebih harus dikode pada subkategori. Penentuan penggunaan subkategori 4-karakter pada B20-B23 atau kode penyebab ganda adalah untuk mengidentifikasi kondisi yang lebih spesifik. Kasus neoplasma baik primer atau sekunder (metastasis) yang merupakan fokus perawatan, harus dicatat dan dikode sebagai diagnosis utama. Contoh: Diagnosis Utama Diagnosis Sekunder Prosedur Dikode diagnosis Neoplasma utama, : Karsinoma mammae - dibuang dua tahun yang lalu: Karsinoma sekunder paru-paru: Bronkoskopi dengan biopsi ganas riwayat paru-paru neoplasma (C78. Diagnosis Sekunder Prosedur:: Cystoscopy: Kanker bladder telah dibuang - dirawat untuk pemeriksaan follow-up dengan Dikode Pemeriksaan follow-up pasca operasi neoplasma ganas (Z08. C80 digunakan sebagai kode diagnosis utama hanya jika dokter dengan jelas mencatat neoplasma ganas tanpa penjelasan lokasinya. Contoh: Diagnosis Utama Diagnosis Sekunder::Multiple myeloma dan adenokarsinoma prostat primer Dikode Neoplasma ganas primer yang independen dengan lokasi multipel (C97) sebagai diagnosis utama, multiple myeloma (C90. Contoh: Diagnosis Utama Diagnosis Sekunder: Gagal ginjal akibat:glomerulonefrosis diabetes Dikode Diabetes Melitus, tidak dijelaskan, dengan komplikasi ginjal (E14. Contoh: Diagnosis Utama Diagnosis Sekunder: Kebutaan karena Katarak:- Dikode Katarak (H26. Kode-kode ini tidak digunakan sebagai diagnosis utama, kecuali jika fokus perawatan adalah untuk mengobati komplikasinya, sekunder contohnya komplikasi dari abortus untuk sebelumnya. Kode tersebut digunakan sebagai diagnosis pada kategori O00-O02 mengidentifikasi komplikasi terkait atau pada kategori O03-O07 untuk memberikan rincian yang lebih lengkap tentang komplikasinya. Perhatikan bahwa istilah inklusi yang disediakan pada subkategori O08 harus disebut ketika menetapkan subkategori karakter keempat pada O03-O07. Contoh: Diagnosis Utama: Aborsi incomplete dengan perforasi uterus Diagnosis Sekunder: Spesialisasi tidak spesifik: Ginekologi (O06. Dikode Aborsi incomplete dengan komplikasi lain dan Kerusakan organ panggul dan jaringan berikut aborsi dan kehamilan ektopik dan molar (O08. Kode lain tidak diperlukan karena aborsi dilakukan pada episode perawatan sebelumnya. Kode-kode O80-O84 digunakan -46- sebagai diagnosis sekunder untuk menunjukkan cara atau jenis kelahiran. Contoh: Diagnosis Utama Diagnosis Sekunder Prosedur rendah Dikode Kelahiran dengan forseps rendah (O81. Contoh: Diagnosis Utama Diagnosis Sekunder persalinan Prosedur: Seksio Sesar Dikode Kegagalan percobaan persalinan (O66. Contoh: Diagnosis Utama: Hamil cukup bulan, melahirkan janin mati 2800gr Diagnosis Sekunder Prosedur:: Kelahiran spontan delivery (Z37. Perhatikan pengecualian berikut: a) Untuk cedera internal yang dicatat bersama dengan hanya cedera permukaan dan/atau luka terbuka, maka pilih cedera internal sebagai diagnosis utama.
Purchase zyban with american express. Symptoms Of Bipolar Disorder -- An Overview.