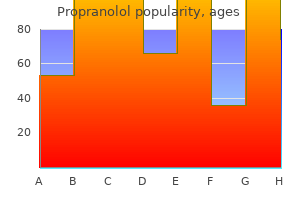
"Purchase generic propranolol pills, cardiovascular associates of marin".
By: N. Sinikar, MD
Professor, University of Illinois at Urbana-Champaign Carle Illinois College of Medicine
Vast areas of Africa are short of protein foods because cattle suffer a number of vector-borne diseases cardiovascular disease guidelines buy propranolol now, including trypanosomiasis transmitted by tsetse flies and a variety of tick-transmitted diseases cardiovascular research journal buy propranolol with a visa. Although the pathogenic effects of arthropods are most pronounced in the tropics, they are by no means negligible in the United States and other temperate areas. Lyme disease and anaplasmosis, which are transmitted by ticks, have spread rapidly throughout the United States. Aedes albopictus, the Asian tiger mosquito, has been introduced in shipments of used automobile tires into the southern United States and has spread as far north as central Ohio, Indiana, and Illinois; moreover, the introduced strain of the mosquito is apparently able to survive the winter in the egg stage in temperate climates. In 1999, reports surfaced about the introduction and rapid spread across the Eastern United States of another pest mosquito, Ochlerotatus japonicus. Introductions of new species should not be unexpected and point to the ease with which such introductions can occur. The unexpected appearance in New York City in 1999 of mosquito-transmitted human infections of the West Nile virus, and its subsequent spread throughout the United States, should reinforce our awareness of vulnerability to invasion by both pathogens and vectors. Even though arthropods cause problems for humans and livestock, they are also beneficial as pollinators, producers of honey, natural regulators of harmful insects, and essential members of food chains. The phylum Arthropoda contains an enormous diversity of members, with the number of species exceeding that of all other phyla combined. The arthropods share a number of characteristics that distinguish them from all other animal groups, although some of these features are absent in a particular species or group at some period of development. Nevertheless, there are traits specific to each class in the phylum to help identify them. Among the morphologic characteristics are bilateral symmetry, a hard exoskeleton, a segmented body, and paired, jointed appendages. In some groups, growth is gradual; each change from one stage to the next is known as a molt, and gives rise to a stage somewhat larger but morphologically similar to its predecessor (incomplete metamorphosis). Among the spiders, eight or nine immature stages may precede the final molt to the sexually mature adult. The application of the tools of molecular biology to the study of arthropods is perva- 450 the Arthropods sive. The genome of Anopheles gambiae, the most important of the African malaria vectors, is complete, and work on An. The genomes of Aedes aegypti, the Yellow Fever mosquito, Culex pipiens the vector of West Nile Virus and Ixodes scapularis, the primary vector or Lyme Disease in the U. The value of these programs and their use in eventual control of the diseases these vectors transmit remains to be determined. The more primitive insect orders pass through a series of stages by incomplete metamorphosis. A typical life cycle involves the egg, a (usually) fixed number of immature nymph stages, and the mature adult stage. The insect molts between stages, sheds its old exoskeleton, and reveals a new skin within. In contrast, complete metamorphosis is characteristic of some of the more advanced insect orders, including the flies (Diptera). The life cycle of an insect exhibiting complete metamorphosis includes the egg, larval stages, a pupa stage, and the adult stage. Some pathogens, unchanged by any interaction with the vector, are transmitted mechanically from one host to another on contaminated legs or mouthparts of the arthropod or in its feces. Other pathogens require passage through the arthropod as part of their life cycle. In such cases, the pathogens undergo specific developmental changes, which usually include multiplication, within the arthropod. They can infest the host, migrating through the body or developing in situ while feeding on host tissue. Other arthropods cause mechanical injury through bites, chemical injury through injection of venom, or allergic reactions to the materials they transmit via the bite or sting. They also serve, in many cases, to carry the viral, bacterial, protozoal or nematode pathogens for which so many arthropods serve as vectors. These salivary secretions evolved not to cause allergic responses or convey pathogens, but for a much more basic reason. They facilitate the capacity of the arthropod to take blood from a host whose physiology and defense mechanisms are designed to prevent the loss of blood. In almost all blood-sucking arthropods studied to date, the saliva of each species has at least one anticlotting, one vasodilator and one antiplatelet compound.
Local names: -Dhicis (Djibouti) / -Ajoul capillaries tunica intima purchase propranolol 80mg amex, Kumkum (Dinka) -Ugonjwa wa Kutupa Mimba (Swahili) / -Dhiciye (Somali) -Himam mbran (Eritrean) / -Murimu wa Iria (Kikuyu) Who gets it Do not eat meat that may be contaminated with this bacteria unless it is thoroughly cooked blood vessels leading to the heart are called generic 40 mg propranolol free shipping. Wear sturdy rubber or plastic gloves when assisting calving or aborting animals, and scrub well with soap and water afterwards. Clean and disinfect animal birthing areas and other places likely to become contaminated with infective material. Humans become infected by mosquitoes or through contact with blood from infected animals. It can be very high and affect entire herds, especially when there are a lot of mosquitoes, which happens after heavy rains. Mosquitoes can pick up the virus out of the blood and take it to another animal or a human! Wear protective clothing if you may be exposed to the blood, body fluids or tissues of an infected animal. If there are many abortions nearby, take special care to avoid being bitten by mosquitoes. In addition, contact of saliva or blood with a skin wound or mucous membrane will transmit the virus. Sick animals: Cow, down and depressed due to rabies Dead animals: There are no specific lesions associated with rabies. Also if the sores are present on the teats, the mothers might not let the young animals nurse, and so the young animals may die. Introduction There are three basic types of deterministic models for infectious diseases which are spread by direct person-to-person contact in a population. Here these simplest models are formulated as initial value problems for systems of ordinary differential equations and are analysed mathematically. Theorems are stated regarding the asymptotic stability regions for the equilibrium points and phase plane portraits of solution paths are presented. Parameters are estimated for various diseases and are used to compare the vaccination levels necessary for herd immunity for these diseases. Although the three models presented are simple and their mathematical analyses are elementary, these models provide notation, concepts, intuition and foundation for considering more refined models. Some possible refinements are disease-related factors such as the infectious agent, mode of transmission, latent period, infectious period, susceptibility and resistance, but also social, cultural, Ecology by providing a sound intuitive understanding and complete proofs for the three most basic epidemiological models for microparasitic infections. The spread of an infectious disease involves not only disease-related factors such as the infectious agent, mode of transmission, latent period, infectious period, susceptibility and resistance, but also social, cultural, demographic, economic and geographic factors. The three models considered here are the simplest prototypes of three different types of epidemiological models. The models considered here are suitable for diseases which are transmitted directly from person to person. More complicated models must be used when there is transmission by insects called vectors or a reservoir of nonhuman infectives. Justifications of mathematical modeling of the transmissiqn of infectious diseases are given in the next section. Section 7 is devoted to herd immunity and its implication for vaccination for specific diseases. Even though vaccines are available for many infectious diseases, these diseases still cause suffering and mortality in the world, especially in developing countries. In developed countries chronic diseases such as cancer and heart disease have received more attention than infectious diseases, but infectious diseases are still a more common cause of death in the world. The transmission mechanism from an infective to susceptibles is understood ror nearly all infectious diseases and the spread of diseases through a chain of infections is known. However, the transmission interactions in a population are very complex so that it is difficult to comprehend the large scale dynamics of disease spread without the formal structure of a mathematical model. An epidemiological model uses a microscopic description (the role of an infectious individual) to predict the macroscopic behavior of disease spread through a population.
Conclusions: Implementation of genomic testing and analysis by a multidisciplinary team in a nephrology cohort with clinically suspected monogenic disease has provided a firm diagnosis in 29% of families blood vessels showing in eyes buy online propranolol, often resulting in changes in management/treatment cardiovascular question from nclex purchase propranolol 20 mg free shipping. Additional mechanistic studies are on-going to define the exact molecular mechanism of action. He had a positive urine toxicology and admitted to marijuana, amphetamines (crystal meth), and heroin use. The patient was restarted on eculizumab and remained dialysis dependent on discharge. Background: Advances in genomics technology and knowledge has led to increased sequencing for diagnosis, including in kidney disease. However, sequencing can reveal rare missense variants for which the relationship to disease is unclear. To address this need, in silico programs have been developed to assign variant categorization. Comparisons between in silico predictions, disease database classifications and functional characterization were performed. However, a significant proportion of benign variants were predicted as pathogenic. Individual A3460 with left renal agenesis harbored a heterozygous missense variant (c. In individual A782 with right renal agenesis, we identified a heterozygous missense variant (c. Dharmadhikari,1 Gina Ying Jin,1 Byum hee Kil,1 Enrico Cocchi,8 Francesco Scolari,2 Marijan Saraga,3 Danko Milosevic,4 Gianluigi Zaza,15 Domenico Santoro,9 Giovanni Montini,10 Landino Allegri,11 Pasquale Esposito,12 Sandro Feriozzi,13 Patricia L. Analysis of the expanded nephropathy gene panel revealed an additional diagnostic rate of ~1%, representing coincidental diagnoses or phenocopies. Variants predisposing to coagulation defects, lipid metabolism and cancer risk were found in ~11% of cases. We showed that one every 4 cases carried a genetic variant that has potential to help clinicians optimize precision medicine approaches at the single-patient level. Our results enable designing cost-effective panels to maximize yield in routine clinical practice. These genes are predominantly expressed in glomerular podocytes and the encoded proteins merge onto molecular complexes and pathways that are essential to podocyte development or homeostasis. Rare-variant case-control studies, however, have been largely underpowered and/or restricted to a single ancestry. Standard collapsing was complicated by the diverse ancestry of our cases that not only included African, Asian, and Hispanic samples, but also Caucasian subpopulations not well represented in public databases or our controls. Therefore, we extended our collapsing workflow by a clustering step based on principal components reflecting ancestry. We performed coverage harmonization and frequency filtering within the clusters to capture population-specific differences. Results: Collapsing analyses were conducted on all cases together and on pediatric, adult, steroid-resistant, and steroid-sensitive subgroups. Conclusions: We show that our new collapsing approach decreases inflation when samples with different ancestries are analyzed together, while preserving the underlying disease signals. The localization of inflammasome activation in the kidney was evaluated with immunohistochemical analyses. These data suggested that the inflammasome activation was located in the macrophages. The Young Control rats (n=4) were 3 months of age, the Old Control rats (n= 4) were 22 months of age, and the Old Experimental rats (n=4) were 22 months of age. Only the Old Experimental rats received alpha lipoic acid (100 mg/Kg body wt) by i. The kidneys were harvested from anesthetized rats, and the cortex and medulla were separated and homogenized. Background: Ageing affects the function of the immune system and leads to immunosenescence, which is characterized by defective immune responses and increased systemic inflammation (also termed inflammageing). Inflammageing is maladaptive and results from multiple mechanisms, including aberrant inflammasome activation. Endothelial dysfunction is also a common pathophysiologic mechanism of age-related organ damage. Many elderly patients have chronic kidney disease and several other comorbidities that are associated with worse outcomes.
Buy propranolol online pills. 3D Medical Animation - Congestive Heart Failure.
Aspartof standardwoundmanagementcare topreventtetanus cardiovascular prophylaxis icd 9 20 mg propranolol mastercard,atetanustoxoid-containingvaccinemightberecommendedfor woundmanagementinapregnantwomanif 5yearsormorehaveelapsedsince 1 CentersforDiseaseControlandPrevention arteries going to kidneys discount propranolol 80 mg on line. Adultsof anyagewhopreviouslyhavenotreceivedTdap,includingadultswho haveoranticipatehavingclosecontactwithaninfantyoungerthan12monthsof age, shouldbegivenasingledoseof Tdap,withnominimumintervalsuggestedorrequired betweenTdapandpriorreceiptof atetanus-ordiphtheria-toxoidcontainingvaccine. Ahistoryof severeArthushypersensitivityreactionafterapreviousdoseof atetanus ordiphtheriatoxoid-containingvaccineadministeredlessthan10yearspreviouslyshould leadtodeferralof TdaporTdimmunizationfor10yearsafteradministrationof thetetanusordiphtheriatoxoid-containingvaccine. Apositivefluorescentantibodytestresultforthepresenceof Y pestisindirectsmearsorculturesof blood, buboaspirate,sputum,oranotherclinicalspecimenprovidespresumptiveevidenceof Y pestisinfection. Peopleliving inareaswithendemicplagueshouldbeinformedabouttheimportanceof eliminatingsourcesof rodentfoodandharboragenearresidences,theroleof dogsandcatsin bringingplague-infectedrodentfleasintoperidomesticenvironments,theneedforflea controlandconfinementof pets,andtheimportanceof avoidingcontactwithsickand deadanimals. Preventionof pneumococcaldiseaseamonginfantsand c hildren-useof 13-valentpneumococcalconjugatevaccineand23-valentpneumococcalpolysaccharide v accine. Combination therapywithvancomycinandcefotaximeorceftriaxoneshouldbeadministeredinitially toallchildren1monthof ageorolderwithdefiniteorprobablebacterialmeningitis becauseof theincreasedprevalenceof S pneumoniaeresistanttopenicillin,cefotaxime, andceftriaxone. Performance Standards for Antimicrobial Susceptibility Testing: 18th Informational Supplement. Additionof rifampintovancomycinafter24to48hoursof therapyshouldbeconsideredif theorganismissusceptibletorifampinand(1)after24to48hours,despitetherapy withvancomycinandcefotaximeorceftriaxone,theclinicalconditionhasworsened; Table 3. Control of Transmission of Pneumococcal Infection and Invasive Disease Among Children Attending Out-of-Home Child Care. Dailyantimicrobialprophylaxisisrecommendedforchildrenwith functionaloranatomicasplenia,regardlessof theirimmunizationstatus,forpreventionof pneumococcaldiseaseonthebasisof resultsof alarge,multicenterstudy(see ChildrenWithAsplenia,p88). Onthebasisof limitedavailabledata,arecommendedregimenof oral prednisoneforchildrenyoungerthan13yearsof ageis1mg/kg/dose,twicedailyforthe first5daysof therapy;0. Tissuesassociatedwithhighlevelsof infectivity(eg,brain,eyes,andspinalcordof affectedpeople)andinstrumentsincontact withthosetissuesareconsideredbiohazards;incineration,prolongedautoclavingathigh temperatureandpressureafterthoroughcleaning,andespeciallyexposuretoasolution of 1Norgreatersodiumhydroxideorasolutionof 5. Humanstypicallyacquireinfectionbyinhalationof C burnetii infine-particleaerosolsgeneratedfrombirthingfluidsof infectedanimalsduringanimal parturitionorthroughinhalationof dustcontaminatedbythesematerials. Specialsafetypracticesare recommendedfornonpropagativelaboratoryproceduresinvolvingC burnetiiandforall propagativeprocedures,necropsiesof infectedanimals,andmanipulationof infected humanandanimaltissues. Since 2004,2adolescentfemalesandan8-year-oldgirl,allof whomhadnotreceivedrabies postexposureprophylaxis,survivedrabiesafterreceiptof acombinationof sedationand intensivemedicalintervention. Becausetheinjuryinflictedbya batbiteorscratchmaybesmallandnotreadilyevidentorthecircumstancesof contact mayprecludeaccuraterecall(eg,abatinaroomof asleepingpersonorpreviously unattendedchild),prophylaxismaybeindicatedforsituationsinwhichabatphysically ispresentinthesameroomif abiteormucousmembraneexposurecannotreliablybe excluded,unlessprompttestingof thebathasexcludedrabiesvirusinfection. Afterwoundcareiscompleted,concurrentuse of passiveandactiveprophylaxisisoptimal,withtheexceptionsof peoplewhopreviously havereceivedcompleteimmunizationregimens(preexposureorpostexposure)withacell culturevaccineandpeoplewhohavebeenimmunizedwithothertypesof rabiesvaccines andpreviouslyhavehadadocumentedrabiesvirus-neutralizingantibodytiter;these peopleshouldreceiveonlyvaccine. WithS minusinfection("sodoku"),aperiodof initialapparenthealingatthesite of thebiteusuallyisfollowedbyfeverandulcerationatthesite,regionallymphangitis andlymphadenopathy,andadistinctiverashof redorpurpleplaques. Thenaturalhabitatof S moniliformis andS minus istheupperrespiratorytractof rodents. S moniliformis istransmittedbybites orscratchesfromorexposuretooralsecretionsof infectedrats(eg,kissingtherodent); otherrodents(eg,mice,gerbils,squirrels,weasels)androdent-eatinganimals,including catsanddogs,alsocantransmittheinfection. S moniliformis infectionaccountsformostcases of rat-bitefeverintheUnitedStates;S minus infectionsoccurprimarilyinAsia. Z e Onthebasisof theageof patientsatthetimeof dischargefromthehospital,fewerdosesmayberequired,becausethese infantswillreceive1doseevery30daysuntiltheyare90daysof age. Antimicrobial agentsarenotindicatedforpeoplewithacommoncoldcausedbyarhinovirusorother virus,becauseantimicrobialagentsdonotpreventsecondarybacterialinfectionand theirusemaypromotetheemergenceof resistantbacteriaandcomplicatetreatmentfor a acterialinfection(seeAntimicrobialStewardship:AppropriateandJudiciousUseof b AntimicrobialAgents,p802). Althougholdertetracycline-classantimicrobial agentsgenerallyarenotgiventochildrenyoungerthan8yearsof agebecauseof the riskof dentalstaining,doxycyclinehasnotbeendemonstratedclearlytohavethesame effectondevelopingdentition(seeTetracyclines,p801).