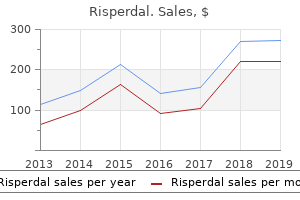
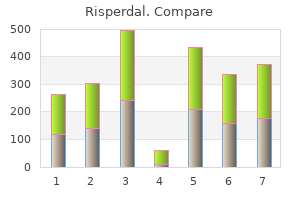
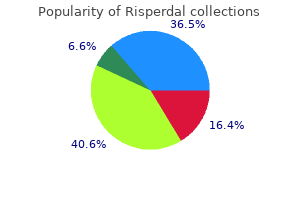
"Best buy risperdal, symptoms jaw cancer".
By: P. Diego, M.A., M.D.
Co-Director, The University of Arizona College of Medicine Phoenix
Most infants are infected during parturition treatment 0f osteoporosis order generic risperdal line, through exposure to infected maternal secretions and blood treatment arthritis 2mg risperdal with mastercard. Approximately 10% of infected infants appear to acquire the infection in utero through hematogenous spread. Although transmission is more likely with a high viral load, babies have been infected after delivery to untreated women with very low levels of viremia. Typically, if a woman is not already on medications, therapy is started in the second trimester and continues throughout pregnancy. Controversy still exists about the role of Cesarean section in these cases, but generally if a woman is adequately treated with good viral suppression and delivery proceeds quickly, vaginal delivery is safe. Women who are untreated or who have prolonged rupture of membranes are offered Cesarean section. A twelve-year-old child presents with a three-day history of cough, chest pain and fever of 101 F. Interstitial markings- (Assess that the students know the difference between interstitial patterns on a chest radiograph vs. Review of Important Concepts: Historical Points What is the time course of disease. What associated symptoms might be relevant, both from the case as given and for additional questions What items in the past medical history, social history or family history might be relevant From the past history, it is important to know if the child has an underlying pulmonary disorder (e. Crackles are more intermittent and are due to opening of smaller airways filled with secretions. Several websites provide sounds for comparison, here are a few to try. The onset is acute rather than indolent, the findings on chest radiographs are lobar consolidation/infiltrates rather than interstitial, and there are few prodromal symptoms such as sore throat and headache, although "typical" pneumonia may follow a viral respiratory illness. The common pathogens are Mycoplasma or Chlamydia pneumoniae (not to be confused with Chlamydia trachomatis). Atypical pneumonia due to Mycoplasma or Chlamydia pneumonia is more common in this age group. They may also develop "typical" pneumonia, although this age group is the least often affected. Viral pneumonia may also occur, although the most common viral pathogen in school age children is influenza, which usually leads to the patient appearing more ill than the child in this case. Neonates are more likely to be affected with organisms acquired during parturition, such as group B Streptococcus or Chlamydia trachomatis. Infants outside the neonatal period may have viral pneumonia or serious bacterial infection with Staphylococcus aureus, Streptococcus pneumoniae (especially if incompletely immunized) or occasionally non-typeable Haemophilus influenzae. Older patients could be treated with a quinolone such as levofloxacin which would cover other agents of community acquired pneumonia, however, they are not labeled for use in growing children because of concerns about effects on cartilage.
The participatory process is to ensure that political treatment regimen generic 3 mg risperdal otc, economic and administrative authority is exercised in a manner that ensures that public resources are managed efficiently and with integrity in response to the problems and critical needs of the people treatment eczema buy 2 mg risperdal fast delivery. These include: conflict of roles between and among the arms of government and governance institutions; resource disparity undermining the role of different arms of government; inadequate participation of civil society in governance processes; little interest of citizens in the democratic processes; and a perception of corruption in the public sector. In view of this, the key areas of policy focus of governance for the medium-term are: deepening the practice of democracy and institutional reforms; local governance and decentralization; public policy management and public sector reform; enhancing development communication; participation of women in governance; corruption and economic crimes; rule of law and justice; public safety and security; access to rights and entitlements; national culture for development; domestic and international relations; migration for development; and evidence-based decisionmaking. Currently however, there are still grey areas and inadequate definition of functions resulting in periodic conflicts between and among them. Resource disparity undermines the role of these different arms of governance; in particular independent governance institutions are generally under-resourced. There are also inadequate transition regulation arrangements in place to effectively manage the transition process during changes in administration. Strategies identified to achieve this objective include the following: review constitutional provisions to ensure clarity of roles and responsibilities of governance institutions and arms of Government; build capacity of governance institutions and Parliament to draft laws and perform oversight responsibilities; establish relative resource parity; and ensure enactment of the Transition Bill. Special attention is to be paid to the work of the Constitutional Review Commission which is tasked with the responsibility of collating views on amendments to the Constitution among other things. Enhancing Civil Society Participation in Governance: the role of civil society as key stakeholders/ partners in the development process is very crucial to achieving transparency and accountability. This is attributed to either lack of interest or that they are not well informed on the democratic process to enable them participate. Their active participation in the governance process would enhance grass-root participation, as well as a "bottom-up" approach to governance, as most civil society organisations are located within communities and are well placed to articulate the views of the local citizenry on governance issues. Their participation also ensures accountability and transparency in governance processes. Promoting Coordination, Harmonization and Ownership of the Development Process: the coordination, harmonization and participation of the general public or ordinary citizens in the policy formulation and dialogue processes are very central to the issue of ownership. There is however the need to coordinate and harmonise the participatory process effectively. Strategies identified to achieve the needed outcomes include: undertake in-depth consultations between and among stakeholders and institutionalize a mutually agreed framework for development dialogue. The Meet the Press series, "Peoples Assemblies", Town Hall Meetings and "Policy Fairs" at all levels are very useful instruments in this regard. Promoting the Participation of State and Non-State Institutions in Governance: Over the years, the participation and involvement of state and non-state institutions in governance have not been adequate. This state of affairs has been generally attributed either to lack of interest or discrimination on the part of the key players and drivers of the process. In order to ensure effective participation of all stakeholders there is the need to make deliberate effort to involve all interest groups in policy processes. Government will continue to organise and expand public 98 policy fairs to engage the citizenry in policy formulation, implementation and evaluation. The main focus of the strategy is to identify, institutionalize and entrench the participation of all institutions and stakeholders, both state and non-state, in the governance process. Strengthening local governance within the concept of democratic principles implies getting the people involved in decision-making, especially grassroots participation to ensure a bottom-up approach to governance. This is necessary to nurture, uphold and entrench the principles of transparency and accountability in governance processes. This additionally implies the need for an effective coordination, communication and harmonization between and of the different levels of Government. This will ensure that the elected representatives of the people are both visible and audible. The policies to strengthen local governance and decentralization are organized under three broad categories, namely: administrative, political and fiscal decentralization. To address these issues, strategies identified include the following: review Acts 656 and 462 and ensure their consistency and harmonization; and finalise and implement the National Decentralization Policy and Plan derived from the decentralization consultations and the National Stakeholders Conference on Decentralization. Mainstreaming Employment into District Economic Development Plans: National macroeconomic policies have not been able to translate relative macroeconomic stability into employment gains successfully. This is aggravated by the inability of district assemblies to mainstream employment issues in their development plans. Strategies identified to ensure creation of employment opportunities especially for the youth at the local level include: provide support to District Assemblies to facilitate, develop and implement employment creation programmes based on their natural resource endowments and competitive advantage. The principal focus of the main strategy identified would therefore seek to institutionalize democratic practices in local government structures. To bridge this information gap, identified strategies to be adopted include the following: fully operationalize the Local Government Act 1993, Act 462 and institute attractive incentives for Assembly members to enable them perform the duties assigned to them under the Act effectively.
Wheezing medicine cards buy generic risperdal 2 mg on-line, decreased air entry symptoms quotes order discount risperdal line, skin findings of atopy and prolonged expiratory phase would indicate underlying asthma, though in some patients with cough-variant asthma, wheezing may not be evident at each visit. In patients with allergic rhinitis, physical exam will reveal pale, blue, swollen nasal mucosa, watery discharge from eye/ nose and allergic shiners. If recurrent sinusitis is the cause of the recurrent cough, then it is important to look for a history of underlying cause such as allergic rhinitis. In a patient with frequent episodes of coughing associated with colds, what would be the next step in management With a clear history and physical exam to support a diagnosis of asthma, a trial of beta agonists (with or without inhaled corticosteroids) can be prescribed for a limited time. Improvement would suggest a diagnosis of asthma, but it is important to establish a definitive diagnosis based on spirometry. It is also reasonable to obtain a chest x-ray in a child with a recurrent cough (may show evidence of hyperinflation and peribrochial thickening in the case of asthma). However, most physicians would do empiric therapy first in an outpatient setting in the face of a clear history and physical exam findings. Empiric therapy should be time limited, the patient should be re-evaluated in 2-4 weeks for improvement and eventually a definitive diagnosis should be established. Once the diagnosis of asthma is established, the patient needs to have an asthma action plan and education on use of various medications, use of inhalers with spacer, avoidance of triggers etc. Is there a place for cough suppressants and other over the counter medications in the management of a chronic recurrent cough She has been feeding a little less than normal and there has been no vomiting or diarrhea. Neonates with fever: What are the age cut-offs we use for fully evaluating serious bacterial infections What are the clinical signs that may be associated with a serious bacterial infection All infants under 8 weeks (56 days) are fully evaluated for serious bacterial infections with temps >100. Infants may exhibit poor feeding, decreased urination, fussiness, lethargy, diarrhea, or may only have fever and otherwise appear fairly well. Serious bacterial infections: Assess that the student knows the major types of serious bacterial infections for which infants undergo evaluation including sepsis, urinary tract infection, meningitis, and pneumonia. The student may also mention herpes simplex virus as causing a serious illness or bacterial gastroenteritis. P a g e 56 this patient needs to be hospitalized, as do all infants with fever under the age of 28 days. This patient should be started on Ampicillin and Gentamicin or Ampicillin and Cefotaxime to cover the pathogens listed above. If a culture is positive, the infant will need to be treated for a longer period of time and the antibiotic used is based on sensitivities from the culture. Suggestions for Learning Activities: Review specific laboratory findings and have the student determine if an infant aged 6 weeks with fever of 101 is low risk utilizing the Philadelphia criteria (or the criteria used at your hospital. Boston or Rochester) Practice writing admission orders for the 2 wk infant in this scenario using a weight of 4 kg. Specifically, ask questions about why a lumbar puncture is necessary and how it is done. Infants with fever: What are the clinical signs that may be associated with a serious bacterial infection The patient could have a serious bacterial infection such as pneumonia, sepsis, meningitis, or a urinary tract infection.
Among the top performers in 2012 are the island economies (Cabo Verde treatment ibs purchase risperdal australia, Mauritius medications zopiclone best order for risperdal, and the Seychelles), which recorded healthy life expectancies of more than 60 years. Some countries saw very little change in healthy life expectancy between 2000 and 2012 (South Africa saw no change at all). Other countries-including some that were in conflict in the 1990s, such as Eritrea and Rwanda (15 years) and Ethiopia (11 years)-recorded significant improvements. Healthy life expectancy is related to four key variables: country income, natural resources, fragility, and landlockedness. There are clear signs of a resource curse in terms of longevity (literacy is also inversely correlated with natural resource endowment) (figure 3. People in upper-middle-income and highincome countries can expect to live in good health 6. For every 10 additional children per 1,000 live births surviving to the age of five, life expectancy increased by 0. In 2000 less than $100 million was disbursed to malaria-endemic countries to fight malaria; in 2013 the figure was $1. As a consequence, the number of children dying from malaria fell dramatically, partly as a result of the expanded use of insecticide-treated bednets. The risk of a child under five dying from malaria is low in Southern Africa (excluding Malawi and Zambia), partly because of climatic conditions. It exceeds 20 deaths per 1,000 live births in Angola (21), Nigeria (24), Guinea and Sierra Leone (27), Chad (28), and the Central African Republic (35). This finding holds even after controlling for other country and household features, suggesting that policy choices underpin this poor health outcome in resource-rich countries. Trends in obesity suggest that poor nutritional habits are accompanying rising incomes. The condition is most prevalent among highly-educated women, women in urban settings, and women in middle-income countries. The figure is likely to reach epidemic proportions in the near future, presenting Africa with a new health challenge (Popkin 2001; Ziraba, Fotso, and Ochako 2009). Early growth retardation also impedes cognitive development and schooling achievements (Dercon and Portner 2014). Unlike in Asia, where there is a strong cultural preference for boys, who are therefore better fed, in Africa boys under five are more malnourished than girls (39. This difference largely reflects biological differences in health and survival between boys and girls (Kraemer 2000; Waldron 1983). If this biological disadvantage is not offset by cultural preferences for boys (as in Asia), higher malnutrition rates among boys result (Wamani and others 2007). The overall level of development of a country matters for child nutrition, though other factors are likely even more important (Harttgen, Klasen, and Vollmer 2013). Children born to educated women enjoy chances of proper growth development that are 9. Children in poor, rural households with undernourished mothers are 20 percent more likely to be stunted. Physical impairment and disability also deprive people of opportunities (capabilities) and the ability to do and be what they value (their functionings) (Mitra 2006). As a group, the disabled are typically either undersampled or poorly identified in representative surveys and as a result often understudied. From a sample of seven countries across Africa on which comparable data are available, it appears that almost 1 working-age adult in 10 in Africa suffers from a disability, defined as reporting severe difficulties in moving about, concentrating, remembering, seeing or recognizing people across the road (while wearing glasses), or taking care of themselves (figure 3. Note: Results are from ordinary least squares regression of an indicator variable of an adult woman being underweight (1 if the body mass index is less than 18.
Best buy risperdal. SPSS for questionnaire analysis: Correlation analysis.