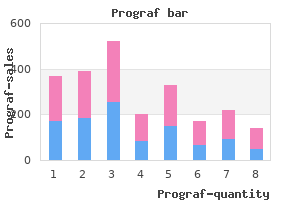
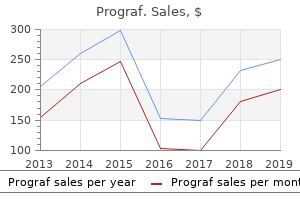
"Buy prograf canada, antiviral used to treat flu".
By: I. Kan, M.B. B.CH., M.B.B.Ch., Ph.D.
Associate Professor, Mayo Clinic College of Medicine
It is also the most technically demanding of the tasks of a district hospital doctor or clinical officer hiv infection rates in the world buy 5mg prograf visa, and is thus a good measure of the quality of his medical education hiv infection rate in ghana prograf 1mg overnight delivery. If this has not been adequate, either because it never was adequate in the medical school, or because the quality of its teaching has fallen, he will be very loath to do much surgery, and may do none. This is why many rural hospitals, and several district hospitals in some countries do little surgery. When this happens, patients soon realize that it is no use going to such hospitals, with the result that they soon have empty beds. So if you see a hospital with empty beds, one of the first questions to ask yourself is: "What is the quality of the surgery here? The constraints on the provision of surgical care are formidable, but some have succeeded in increasing their work-load and their operations tally despite rising costs and scarce manpower resources. Ethiopia and Paraguay, for example, are about as different as two countries could be. Typically, the people of low-income countries are poor, hungry, and rural, although they are rapidly migrating to the towns. Meanwhile its per capita food production and its already meagre gross national product even if increasing remains hugely unevenly distributed, whilst costs on the military and socially dislocating wars multiply. These typically have between 60 and 200 beds and are staffed by 2-4 doctors, assisted by nurses and auxiliaries. Each hospital typically serves about 150-250,000 people living in an area which may be as large as 3,000 square miles. Over the world as a whole these hospitals range from the excellent to the indescribable. At one end they provide care which anyone would be fortunate to have, at the other the few patients brave (or foolish) enough to enter them lie largely untended. Nonetheless these hospitals are the local focus of health care in the community and have an important place as such, as well as being a major employer of labour. If you work in a hospital in the middle or at the lower end of this spectrum, expect to find your wards overcrowded, with more than one patient in a bed. Your maternity ward is likely to be particularly overcrowded, and resist all your attempts to decongest it. Cultural reasons may make it impossible to restrict the number of visitors to the wards. If your hospital is at sea level on the equator, expect to operate at 300C in 95% humidity, your clothes wet, and everything which can go rusty or mouldy doing so. This is somewhat better than the average conditions for SubSaharan Africa at the time of writing. You will see that there are several patients on traction, two with long leg casts, and that one of the beds contains 2 patients. However, on occasion expect to find no water, no steam, no linen, no gauze, no bandages, no sutures, no local anaesthetics, no gloves (or only gloves with holes in them), no plaster, (or only plaster that does not set) or no intravenous fluids. When you need to prepare for a laparotomy expect that no instruments have been prepared beforehand. When you go into the maternity ward late one night, be prepared for the last sphygmomanometer to be missing. Try not to blame your staff too harshly, they may not be responsible; and even if they are, their families may be starving. Try to examine where things need to be changed and call meetings to get these things done. If you do have electricity, be prepared for it to fail at 3am, just when you are in the middle of a Caesarean section. You may, however, have more than the teaching hospital: it too maybe without water, electricity, spirit, or linen! You may be cherished, supported, praised, and congratulated by your Ministry of Health, or you may not.
Blood Vessels Functional classification the blood vessels hiv infection diagnosis and treatment order prograf online pills, together with the four chambers of the heart hiv aids infection rates uk prograf 5mg on line, from a closed system for the flow of blood; only if there 269 Human Anatomy and Physiology is an injury to some part of the wall of this system does any blood escape. Arteries carry blood from the ventricles (pumping chambers) of the heart out to the capillaries in organs and tissue. Veins drain capillaries in the tissues and organs and return the blood to the heart. Capillaries allow for exchanges between the blood and body cells, or between the blood and air in the lung tissues. Note smooth muscle is found in the middle layer or tunica media of arteries and veins. Because the thicker muscle layer in the artery wall is able to resist great pressures generated by ventricular systole. In arteries, the tunica medial plays a critical role in maintaining blood pressure and controlling blood distribution in the body. This is 270 Human Anatomy and Physiology a smooth muscle, so it is controlled by the autonomic nervous system. A thin layer of elastic and white fibrous tissue covers an inner layer of endothelial cells called the tunica interna in arteries and veins. The tunica interna is actually a single layer of squamous epithelial cells called endothelium that lines the inner surface of the entire circulatory system. As you can see in Figure 9-7, veins have a unique structural feature not present in arteries. When a surgeon cuts into the body, only arteries, arterioles, veins, and venules can be seen. The most important structural feature of capillaries is their extreme thinness-only one layer of flat, endothelial cells composes the capillary membrane. Instead of three layers or coats, the capillary wall is composed of only one-the tunica interna. Substances such as glucose, oxygen, and wastes can quickly pass through it on their way to or from the cells. Smooth muscle cells that are called precapillary sphincters guard the entrance to the capillary and determine into which capillary blood will flow. It continues down behind the heart just in front of the vertebral column, through the diaphragm, and into the abdomen (Figure 9-8 and 9-9). The thoracic aorta lies just in front of the vertebral column behind the heart and in the space behind the pleura. The abdominal aorta is the longest section of the aorta, spanning the abdominal cavity. The thoracic and abdominal aorta together makes up the descending aorta 272 Human Anatomy and Physiology Figure 9-7. Sections of small blood vessels showing the thick arterial walls and the thin walls of veins and capillaries. These from a crown around the base of the heart and give off branches to all parts of the myocardium. Branches of the Aortic Arch the arch of aorta, located immediately beyond the ascending aorta, gives off three large branches. After extending upward somewhat less than 5 cm (2 inches), it divides into the right subclavian artery, which supplies the right side of the head and the neck. The left common carotid artery extends upward from the highest part of the aortic arch. The left subclavian artery extends under the left collar bone (clavicle) and supplies the left upper extremity. Branches of the Thoracic Aorta the third part of the aorta supplies branches to the chest wall, to the esophagus, and to the bronchi and their treelike subdivisions in the lungs. There are usually nine to ten pairs of intercostal 274 Human Anatomy and Physiology arteries that extend between the ribs, sending branches to the muscles and other structures of the chest wall.
This should include evidence of retroplacental clots antiviral drugs for chickenpox purchase prograf 1mg otc, or vaginal bleeding accompanied by a worrying foetal status or a hypertonic uterus antiviral us release generic 1mg prograf otc, together with ultrasound visualisation of the abruption. So aim for a vaginal delivery if the foetus has died as soon as you make the diagnosis. The foetus is often dead, and is usually growth-retarded and premature, so cephalopelvic disproportion is seldom a problem. Insert a urinary catheter and monitor the urinary output, which should be >50ml/hr. Stimulate labour with an oxytocin infusion, unless there is a previous Caesarean scar, or the patient is para 2. If the cervix is unripe, insert 200g misoprostol rectally (not vaginally as it may be washed out) but then do not use oxytocin within 3hrs of misoprostol. If the foetus is already dead, which is often the case, expedite delivery by attaching clamps on its head, or inserting a Foley catheter in the foetal rectum. Inflate the balloon with 50ml water in the case of the breech presentation, and apply steady traction with the help of a weight and rope (21. If the patient is obese or a multipara, with an unfavourable cervix, she is particularly at risk; assess the progress of labour by careful vaginal examination. The 2nd stage is usually rapid: the dead baby, the placenta, and clot may however all be expelled suddenly, and tear the vagina, perineum, or cervix. After delivery of the placenta, there are often problems, because of a clotting defect, and because there may be an atonic uterus. A short period of inattention might result in relaxation of the uterus and the loss of a critical quantity of clotting factors. Failure to progress, despite artificial rupture of her membranes, oxytocin and traction. If bleeding does not stop after emptying the uterus, deliver it out of the abdominal wound and administer oxytocin and misoprostol. If bleeding continues, put a tourniquet round the lower segment using a rubber urinary catheter (22. This may give you time to replenish the circulation, organise blood transfusion, and for the clotting factors to recover. If bleeding continues, apply a B-Lynch suture (22-13) and if necessary ligate the uterine arteries (22-14) or proceed to hysterectomy (21. How best you should do this, and what methods you should use, depends greatly on where she is. This has been beautifully described: Obstetrically, there are now two worlds, with pockets of one world in the other, and every gradation between the two. In the advantaged industrial world Caesarean Section is now so safe that it has done much to change the whole pattern of obstetrics there. In that world obstetric services are good, and theatres and blood banks well organised. If a woman needs a Caesarean Section, it is done by a skilled obstetrician and an experienced anaesthetist. Antenatal care is available everywhere, transport is easy, and most women are sufficiently educated to understand why they should have a hospital delivery if they need one. Most of them only plan to have 2 or 3 children anyway, and are not frightened by the possibility that Caesarean Section might reduce their chances of having any more. Just because it is so safe, it is used electively for up to even 40% of women as a means of anticipating difficulty, rather than dealing with disaster. It is done so efficiently that seriously traumatic vaginal deliveries and perinatal deaths from birth injury have almost disappeared. A really disadvantaged woman must have 6-7 children, in order to be sure that 3 or 4 will survive. If she has an obstructed labour in a distant village, she may arrive in your hospital after a long journey, dehydrated, ketotic, shocked, anaemic, or infected, or all of these things. If you have to perform a Caesarean Section, you may have to do it through infected tissues, so that it may be followed by peritonitis, which antibiotics may fail to control. When she has recovered, she may remember only a frightening operation followed by a difficult puerperium, and deliberately not seek hospital care when she becomes pregnant again. If the foetus died, she may blame the hospital for the death, and decide to have the next one at home.
Syndromes
- Spleen problems
- 1,000 to 1,500 IU/day for infants
- Roach powders
- Rapid, weak pulse
- Acne
- Curving of the spine (kyphoscoliosis)
- Stomach pain
This will leave a defect in the base of the caecum: if the margins are healthy hiv infection per capita prograf 5mg amex, insert a purse string suture around the edge of the defect and invert it hiv stages after infection buy discount prograf 5mg line. If the edges are unhealthy, and will not take a suture, make sure you have good enough exposure (if necessary, extend the incision) and remove more of the caecal base till you reach healthy tissue and close the bowel formally. Secure some omentum over the repair, insert a drain adjacent to it, close the muscles of the abdominal wall, but leave the skin open. If the appendix is buried in a mass of adhesions and pockets of pus, avoid spreading the infection. Enlarge the incision, lift its medial side forwards, isolate the mass with warm packs, suck out the pus, and remove the appendix if this is not too difficult. If you lose the appendix stump or appendicular artery, enlarge the incision and withdraw the caecum into the wound once more to find the culprit. If you find a tumour in the caecum, make a midline incision and perform a right hemicolectomy (12. No further treatment is necessary apart from the appendicectomy, unless there are metastases in the liver. If you find a mucocoele of the appendix, make a midline incision and perform an ileocaecal resection, together with a right oophorectomy (in a woman) and excision of any involved peritoneal surface. If there are enlarged mesenteric nodes, and a clear yellowish serous exudate, suspect mesenteric adenitis, and close. If you can feel a tensely distended gall bladder when you pass your finger up through the incision, this may be due to cholecystitis or an obstructed gallbladder. Do not be tempted to perform a cholecystectomy via a small incision in the right iliac fossa! If you make a formal laparotomy incision, do not remove a normal appendix, but tell the patient the appendix remains in situ! Locate the caecum, find the artery and tie it, or deal with the ectopic gestation (20. If necessary, drain the abscess, insert a nasogastric tube and manage conservatively (12. If there is tenderness and guarding, reopen the abdomen by a long midline incision and drain the pus. If a faecal fistula develops, it will probably heal spontaneously in 2-3wks, provided there is no distal obstruction (11. If it persists, suspect tuberculosis, amoebic colitis, actinomycosis, or a retained foreign body (a faecolith or retained swab). If the temperature rises in the 2nd week, accompanied by malaise and local symptoms, there is probably pus somewhere. If there is a mucous rectal discharge or diarrhoea, suspect that there is pus in the rectovesical pouch. If the wound continues to discharge, there may be a nonabsorbable suture left behind. If the appendix has a tumour found on histology, ileocaecal resection is only necessary if it was not completely removed or within 2cm of the resection margin. If a hernia develops in the right lower abdomen, there is probably a small defect in the closure and you should repair this to avoid bowel strangulation (18. They are difficult to treat, needing steroids, sulfasalazine or azathioprine, but fortunately are uncommon in the low and middle-income countries. Remember that and radiation >30Gray can also cause i R 276 277 Remember that schistosomiasis, paracoccidiomycosis and radiation >30Gray can also cause inflammatory bowel disease. Schistosomiasis of all types can cause, in the acute phase, a florid ulcerative enterocolitis with perforation, and with chronic infestation, granulomata, fibrotic strictures and polyps anywhere in the gastro-intestinal tract, but especially in the colon. These may result in chronic stricture, intussusception, fistulae and rectal prolapse from persistent straining. Campylobacter jejuni affects the caecum and causes lymphadenitis in the terminal ileal mesentery; Yersinia enterocoli affects the terminal ileum with similar lymphadenitis.
Buy 0.5 mg prograf with amex. Ending the HIV Epidemic March 2019 Vital Signs.