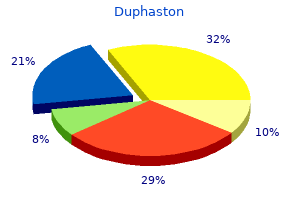
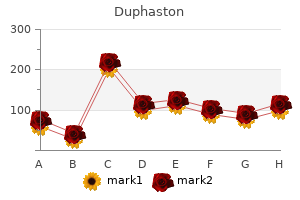
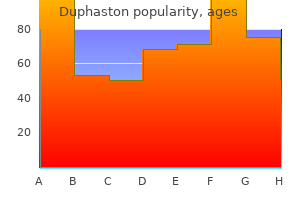
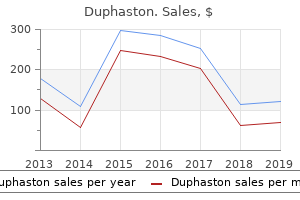
"Purchase genuine duphaston, breast cancer 4th stage survival rate".
By: U. Uruk, M.A., M.D., M.P.H.
Clinical Director, Marian University College of Osteopathic Medicine
However menopause 55 plus purchase 10 mg duphaston with amex, "compressing" bone fragments has not proved more effective than ensuring passive contact and stability at the fracture site through use of locking plates menopause odor change cheap duphaston 10 mg overnight delivery. Metal Plating Metal plating systems are most commonly titanium alloys with proven biocompatibility and strength. These systems all have generally analogous application, but are not interchangeable among manufacturers. These systems also have generally analogous application but are not interchangeable. Surgical delay in the management of dog bite injuries in children, does it increase the risk of infection? Defense Centers of Excellence for Psychological Health and Traumatic Brain Injury. The evolution of military trauma and critical care medicine: Applications for civilian medical care systems. Because of the thick bone of the anterior wall of the sinus as well as its curved convexity, this first barrier to the effects of cranial trauma resists fracture. The posterior wall has a central spine that projects intracranially, upon which lies the superior sagittal sinus. This venous sinus begins as a superior extension of the dorsal nasal vein of the nose as it penetrates the foramen caecum. The sinus volume increases as it courses over the convexity of the brain (Figure 3. The frontal sinus mucosa has a peculiar characteristic of forming cystic structures when injured. These mucoceles have a tendency to erode bone probably as an osteoclastic response to the pressure exerted by the cyst. Very often the patients presenting with a fracture of the frontal sinus are victims of violent crime, gunshot wounds, or industrial accidents. The infraorbital nerve may have been traumatized during the traumatic event, and the patient may complain of forehead numbness. Conversely, if the fracture is depressed, it will appear as a distinct depression in the area of fracture. However, if the patient is seen sometime after the occurrence of the injury, the depression may fill with blood, and the displaced area will be effaced. Though the actual fracture may not be seen, an opacified frontal sinus that does not clear in 2 weeks raises a strong suspicion of disruption of the duct. The anterior wall, floor, and posterior wall are fractured, and the corner fracture is normally in continuity with a more extensive fracture to the frontal bone. Through-and-Through Fractures the through-and-through fracture is the most serious of all frontal sinus fractures. It is a compound comminuted fracture involving the anterior and posterior walls, entering the anterior cranial fossa (Figure 3. Approximately 50 percent of patients die at the scene of the injury or in the first 24 hours of hospitalization. Characteristically the head and neck surgeon does not meet the patients until they arrive in the operating room at the behest of the operating neurological surgeon, who is busy stopping intracerebral bleeding and debriding the wound. A bicoronal scalp incision has already been made, the fractured skull fragments have been removed, and the injury has been exposed. Anterior Wall Fractures Nondisplaced frontal sinus fractures do not require any surgical intervention. The most important is that if there is any entrapped mucosa between the edges of the fracture, there is the potential to develop a mucocele. If the fracture is compounded, it can sometimes be reduced through an overlying laceration. The coronal scalp flap provides the best surgical exposure and is the most commonly used. Posterior Wall Fractures Management of posterior wall fractures is the most controversial of all the fracture sites. If any doubt concerning posterior wall displacement exists, frontal sinus exploration is indicated. This is usually done through a coronal scalp incision, then creating an osteoplastic bone flap of the anterior wall of the frontal sinus. A clear view of the interior of the sinus is obtained, and any disruption of the posterior wall is identified.
As with any form of ventilation breast cancer kamikaze cheap duphaston 10mg without prescription, positive pressure can result in a pneumothorax on the contralateral side menstrual joke purchase duphaston 10 mg line, which must be carefully observed for. Pulmonary hypoplasia and immaturity of the lungs remain the leading cause of death, from pulmonary hypertension (right-to-left shunting) with resultant hypoxemia. The old management strategy of immediate surgery is now replaced by the principle of physiologic stabilization and delayed surgery. Conventional ventilatory techniques, with high pressures and hyperventilation used to reverse ductal shunting and cause alkalinization, are now being replaced with ventilatory techniques utilizing the concepts of permissive hypercapnia and high frequency oscillation ventilation. The complications of ventilation including air leaks, barotrauma and consequent bronchopulmonary dysplasia are at least in part circumvented because of these newer techniques. Regardless of the treatment, the goal is to reverse the persistent pulmonary hypertension causing right to left shunting through the ductus arteriosus and foramen ovale. Endogenous nitric oxide is an important modulator of vascular tone in the pulmonary circulation. Initial studies indicated that inhalation of nitric oxide results in a reduction in pulmonary hypertension, with improvement in oxygenation but no change in the systemic vascular resistance. However, no such beneficial effect has as yet been consistently reported in infants with congenital diaphragmatic hernia. Inhaled nitric oxide has side effects, although those due to nitrogen dioxide and methemoglobin formation can be minimized by using the smallest effective nitric oxide dose, continuous nitric oxide and nitrogen dioxide monitoring and frequent methemoglobin analyses. Bypass is continued until the pulmonary hypertension is reversed and lung function is improved, usually between 7 and 10 days of age. Despite this aggressive therapy, there are newborns with such severe pulmonary hypoplasia that all forms of life support are futile. However, if a large portion of the diaphragm is missing, prosthetic material must be used to repair the defect. A chest tube is usually placed in the left hemithorax and brought out through an intercostal space. As the abdominal contents have been in the thorax for most of fetal development, the abdomen often does not have enough room for the "missing" contents. Forcing the contents into the abdomen will compress the vena cava and compromise respirations by pushing up on the diaphragm. The surgeon may be forced to omit total anatomic closure of the abdominal wall, and utilize skin flaps with only the skin being closed. An alternative is to create a silastic silo like those used for gastroschisis or a large omphalocele (see Gastroschisis and Omphalocele chapter). The pouch created accommodates the intra-abdominal organs, and diaphragmatic action and venous return are unimpeded. The final repair is completed after the infant has been weaned off the ventilator and is clinically stable. Fetal surgery for congenital diaphragmatic hernia and other fetal conditions has been considered. Although one may expect a poorer outcome with earlier intrauterine diagnosis, ultrasound, diagnosis before 25 weeks of gestation was not found to be a uniformly bad prognostic indicator (median mortality, 60%). However, outcome was worse for those fetuses with other congenital anomalies (median mortality, 93%). Many of these patients require bronchodilators, oxygen, diuretics, and corticosteroids for obstructive airway disease and bronchopulmonary dysplasia. Endotracheal intubation with gentle ventilation, followed by nasogastric suctioning is immediately indicated. Pulmonary hypoplasia and pulmonary hypertension with right-to-left shunting are common with resultant hypoxemia. The surgeon does not need to worry about medical problems as the neonatologist will already have treated them. High frequency oscillatory ventilation during repair of neonatal congenital diaphragmatic hernia. Impact of delayed repair and elective high-frequency oscillatory ventilation on survival of antenatally diagnosed congenital diaphragmatic hernia: first application of these strategies in the more "severe" subgroup of antenatally diagnosed newborns.
Biological Data Records All disease outbreaks consist of three main components: a susceptible host population womens health 30 day bikini diet cheap 10 mg duphaston with visa, a disease agent interface womens health expo kingston generic duphaston 10 mg mastercard, and the environment in which the host and agent interact in a manner that results in disease. Disease contingency plans expedite these efforts by providing basic information about the distribution and types of animal populations in the area, animal movement patterns, any history of disease problems on the area, and general environmental features. This information, along with facts gathered at the time of a disease outbreak, provides a profile for biological assessment and a basis for specific disease control actions. Knowledge of the types of disease problems that have occurred in the area, their general locations, the month and year when they occurred, the species affected, and the genA B Figure 4. Waterfowl die-offs are used to illustrate specific approaches to addressing these common factors. For large mammals, their size and weight pose additional needs regarding carcass transport and disposal. Problem Identification Early detection and rapid and accurate assessment of the causes of disease problems are essential to effective disease control operations. This is accomplished through surveillance of animal populations to detect sick and dead wildlife, and the prompt submission of specimens to qualified disease diagnostic facilities. The speed with which large numbers of animals can become exposed to disease agents and the differences in control activities required for different types of disease problems place a premium on both the speed and accuracy of diagnostic assessments. Once a disease problem has been identified, the following basic activities are carried out. Carcass Removal: Protective Clothing and Supplies Wildlife that have died from disease are often a primary source of the disease agent, and for most situations their carcasses need to be removed from the environment to prevent disease transmission to other animals through contact with or consumption of the carcass. Disease organisms released from tissues and body fluids as carcasses decompose also contaminate the environment. Some disease-causing viruses and bacteria can survive for several weeks or longer in pond water, mud, and soil. Because carcass collection concentrates diseased material in a small area, it is essential that carcasses be handled so that they do not release infectious agents into the environment or jeopardize the health of personnel. Great care also needs to be taken to prevent mechanical movement of the disease agent from the problem area to other areas. Personnel assigned to this task need to wear outer garments that provide a protective barrier against direct contact with disease organisms and that can be disinfected and removed before personnel leave the area. Typically, these include boots, coveralls or raingear, gloves, and a head covering. Use disposable coveralls and outer gloves when possible; the durability and cost of garments are considerations in decisions about whether or not disposable garments will be used. Personnel should remove coveralls and outer gloves before they leave the area, and the garments should be destroyed if they are disposable or they should be doublebagged before they are transported to a location where they can be thoroughly washed before they are reused. Dishwashing gloves, work gloves, and other types of rubber gloves are readily available at hardware and other retail stores, as are scrub brushes for cleaning. Plastic body bags used by the military are excellent for containing wildlife carcasses. Plastic garbage cans lined with commercially available heavy-gauge leaf and litter plastic bags are also excellent containers for transporting carcasses. These containers are especially useful when personnel collect bird carcasses by boat. Tie the bags shut and secure garbage can lids when transporting these containers to carcass disposal sites. Pickup trucks and other four-wheel vehicles are also indispensable under some field conditions. Dogs have been used extensively in wildlife management, and they are a valuable search tool when they are appropriately chosen and handled. Use dogs whenever possible to locate carcasses if there is no disease risk to them. Infectious diseases of wild North American birds do not pose a significant health threat to dogs. Determine disease risk on a caseby-case basis by consulting with wildlife disease specialists. The contingency plan should identify sources of various equipment, whether equipment can be borrowed or rented, and contact persons and their telephone numbers. Commonly used supplies and equipment needed to support disease control operations are summarized in Table 4. Carcass Disposal the primary goal of carcass disposal is to prevent spread of the disease agent to other animals through environmental contamination.
It has been claimed as a reliable test of posterior column function of the spinal cord breast cancer zip hoodie order duphaston without a prescription. Errors in this test correlate with central conduction times and vibration perception threshold women's health clinic melbourne pap smear discount duphaston 10 mg visa. The utility of testing tactile perception of direction of scratch as a sensitive clinical sign of posterior column dysfunction in spinal cord disorders. A reappraisal of "direction of scratch" test: using somatosensory evoked potentials and vibration perception. Seizure morphology may be helpful in establishing aetiology and/or focus of onset. Otherwise, as for idiopathic generalized epilepsies, various antiepileptic medications are available. Best treated with psychological approaches or drug treatment of underlying affective disorders; antiepileptic medications are best avoided. The differentiation of epileptic from non-epileptic seizures may be difficult; it is sometimes helpful to see a video recording of the attacks or to undertake in-patient video-telemetry. This pattern is highly suggestive of a foramen magnum lesion, usually a tumour but sometimes demyelination or other intrinsic inflammatory disorder, sequentially affecting the lamination of corticospinal fibres in the medullary pyramids. Cross References Hemiparesis; Paresis; Quadriparesis, Quadriplegia Setting Sun Sign the setting sun sign, or sunset sign, consists of tonic downward deviation of the eyes with retraction of the upper eyelids exposing the sclera. Setting sun sign is a sign of dorsal midbrain compression in children with untreated hydrocephalus. Metallic poisonings (mercury, bismuth, lead) may also produce marked salivation (ptyalism). Recently, the use of intraparotid injections of botulinum toxin has been found useful. Botulinum toxin treatment of sialorrhoea: comparing different therapeutic preparations. Cross References Bulbar palsy; Parkinsonism Sighing Occasional deep involuntary sighs may occur in multiple system atrophy. Sighing is also a feature, along with yawning, of the early (diencephalic) stage of central herniation of the brainstem with an otherwise normal respiratory pattern. Recognition of single objects is preserved; this is likened to having a fragment or island of clear vision which may shift from region to region. There may be inability to localize stimuli even when they are seen, manifest as visual disorientation. Ventral: A limitation in the number of objects which can be recognized in unit time, i. Ventral simultanagnosia is most evident during reading which is severely impaired and empirically this may be the same impairment as seen in pure alexia; otherwise deficits may not be evident, unlike dorsal simultanagnosia. Visual agnosia: disorders of object recognition and what they tell us about normal vision. This is thought to reflect damage to otolith-ocular pathways or vestibulo-ocular pathways. Skew deviation has been associated with posterior fossa lesions, from midbrain to medulla. Ipsiversive skew deviation (ipsilateral eye lowermost) has been associated with caudal pontomedullary lesions, whereas contraversive skew (contralateral eye lowermost) occurs with rostral pontomesencephalic lesions, indicating that skew type has localizing value.
Buy discount duphaston 10mg on-line. Jeevanarekha Women's Health | Vaginal Discharge | 20th September 2016 | జీవనరేఖ ఉమెన్స్ హెల్త్.