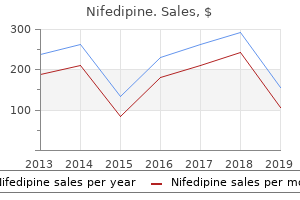
"30mg nifedipine sale, arrhythmia vs palpitations".
By: Q. Rhobar, M.B. B.CH., M.B.B.Ch., Ph.D.
Vice Chair, Wake Forest School of Medicine
Acquired mutation in p53 is the most common genetic alteration found in human cancer (>50%); germline mutation in p53 is the causative genetic lesion of the Li-Fraumeni familial cancer syndrome blood pressure medication ziac purchase generic nifedipine on line. In many tumors blood pressure chart in excel cheap nifedipine online master card, one p53 allele on chromosome 17p is deleted and the other is mutated. This genomic instability greatly increases the probability that p53 null cells will acquire additional mutations and become malignant. In summary, it is likely that all human cancers have genetic alterations that inactivate the Rb and p53 tumor-suppressor pathways. Tumors expressing mutant p53 are more resistant to radiation therapy and chemotherapy than tumors with wild-type p53. If the transcriptional functions of the mutant p53 could be reestablished in tumor cells, massive apoptosis might ensue, whereas normal cells would be protected because they express very low levels of wildtype p53. Investigators have screened chemical libraries for compounds that inhibit tumor cell growth in a mutant p53-dependent manner. One compound entered cells and induced mutant p53 to adopt an active conformation such that p53-dependent transcriptional activation was restored and apoptosis was selectively induced. Other investigators have identified a low-molecular-weight, cell-permeable compound that 1. This causes dissociation of p53 from mdm2, leading to increased p53 protein levels and transcription of genes leading to cell cycle arrest (p21Cip1/Waf1) or apoptosis (e. A second mechanism of p53 induction is activated by oncogenes such as Myc, which promote aberrant G1/S transition. This oncogene checkpoint leads to the death or senescence (an irreversible arrest in G1 of the cell cycle) of renegade cells that attempt to enter S-phase without appropriate physiologic signals. This compound protected mice from the toxic effects of radiation therapy and chemotherapy, including bone marrow suppression, gastrointestinal dysfunction, and hair loss. Taken together, these approaches provide proof of principle for the pharmacologic manipulation of p53 function (mutant or wild-type) that could greatly enhance therapeutic efficacy while decreasing toxicity. Knowledge of the molecular events governing cell cycle regulation has led to the development of viruses that replicate selectively in tumor cells with defined genetic lesions. The former group includes an adenovirus mutant in which the viral p55 protein (which binds and inhibits p53) was deleted; this virus selectively replicates in tumor cells lacking p53 function. More than 90% of human cancers express high levels of telomerase that prevent telomere exhaustion and allow indefinite cell proliferation. In vitro experiments indicate that inhibition of telomerase activity leads to tumor cell apoptosis. Major efforts are underway to develop methods to inhibit telomerase activity in cancer cells. The reverse transcriptase activity of telomerase is a prime target for small-molecule pharmaceuticals. However, in many human cancers, tyrosine kinases or components of their downstream pathways are activated by mutation, gene amplification, or chromosomal translocations. Because these pathways regulate proliferation, survival, migration, and angiogenesis, they have been identified as important targets for cancer therapeutics. The ability to bypass telomerebased growth limitations is thought to be a critical step in the evolution of most malignancies. Most normal somatic cells do not express sufficient telomerase to prevent telomere attrition with each cell division. Many activated kinases and transcription factors migrate into the nucleus where they regulate gene transcription, thus completing the path from extracellular signals, such as growth factors, to a change in cell phenotype, such as induction of differentiation or cell proliferation. Inhibitors of many of these pathways have been developed for the treatment of human cancers. Examples of inhibitors that are currently being evaluated in clinical trials are shown in purple. The deregulated tyrosine kinase activity of Bcr-Abl is required for its transforming activity. The Abl tyrosine kinase inhibitor, imatinib mesylate (Gleevec), has validated the concept of a molecularly targeted approach to cancer treatment.
If pregnancy or a positive pregnancy test does occur in a study subject or the partner of a male study subject during study participation arrhythmia recognition posters discount generic nifedipine uk, lenalidomide must be immediately discontinued arteria lumbalis effective nifedipine 30mg. Potential Drug Interactions: Periodic monitoring of digoxin levels is recommended during co-administration with lenalidomide. The patient will be required to receive counseling every 28 days during treatment with lenalidomide, follow the pregnancy testing and birth control requirements of the program that are appropriate in order to take the telephone surveys regarding compliance with the program. Biologics will verify the authorization number and complete the patient counseling. Patients will be provided with instructions from Biologics with each new dispense on the procedures for return of any unused Revlimid? capsules. Additionally, the treating physician may discontinue therapy with reasonable justification. After randomization, patients who stop therapy for any reason prior to two years from initiation will continue to be followed per protocol for 3 years post maintenance initiation unless the patient withdraws consent for study follow up. This includes patients in whom routine electrophoresis is negative but in whom immunofixation has not been performed. Definite increase in the size of existing bone lesions or soft tissue plasmacytomas. Development of a compression fracture does not exclude continued response and may not indicate progression. Assessment of disease response will be done immediately prior to randomization, prior to cycles 3, 6, and then every 3 months until approximately 22 months from randomization or evidence of disease progression. Additionally, assessments of disease response will be conducted at 6, 12, and 24 months post-transplant. The cumulative incidence of myeloma progression will be compared between vaccine and no-vaccine arms combined. Patients alive without disease progression at last contact are considered censored for this event. The proportion of patients developing Grade 3 toxicity will be compared between the vaccine and no-vaccine arms combined until disease progression or end of follow up. The proportion of patients in each treatment arm with these infections will be compared from randomization until disease progression or end of follow up. Progression-free survival Patients are considered a failure of this endpoint if they die or suffer from disease progression. The time to this event is the time from randomization to progression, death, initiation of nonprotocol anti myeloma therapy, loss to follow up or end of study whichever comes first and it will be compared between the vaccine and no-vaccine arms combined from time of randomization. The time to this event is the time from randomization to death, loss to follow-up or the end of the study, whichever comes first. Overall survival will be compared between the vaccine and no-vaccine arms combined from time of randomization. Myeloma-Reactive T-cells the percent of patients achieving at least a 10-fold increase in tumor-reactive T cells will be compared between the vaccine and no-vaccine arms separately as described above. Quantification of T-cell subsets: Quantification of regulatory T cells and activated memory effector cells will be performed at the serial time points (Appendix C). Peripheral blood will be transported for a cell based assay to assess the kinetics, magnitude and specificity of vaccine-induced myeloma specific plasmablast responses, as detailed in Appendix C. Enrollment Procedures Patients are enrolled in to the Segment A prior to initial systemic therapy (<1 cycle) and first autologous transplant. At the time of enrollment, an authorized user at the clinical center completes the demographics and primary eligibility form which includes questions confirming that the patient signed the consent and meets the eligibility criteria for study entry. Patients must be successfully enrolled in Segment A prior the collection of tumor cells. Once the patient is enrolled in the study (Eligibility Form, Segment A competed): 1. Following enrollment and tumor cell collection the patient should proceed with initial systemic therapy and autologous transplant. Patient will be seen 14 days or less prior to randomization for eligibility assessments prior to randomization/enrollment in Segment B. The pre-randomization disease response assessment must be performed < 10 days prior to randomization. An authorized user at the clinical center completes a checklist confirming that the patient is eligible to proceed to the next stage of treatment on the study.
Procedures specified by manufacturer to evaluate critical operating characteristics of test system blood pressure 9862 buy cheap nifedipine 20mg on line. When limit is exceeded blood pressure in pregnancy order 20 mg nifedipine fast delivery, must determine if due to medical change in patient or lab error. Requirements for patient preparation, specimen collection, labeling, storage, preservation, transportation, processing, referral & criteria for specimen acceptability & rejection 2. Procedures for microscopic examinations, including detection of inadequately prepared slides 3. Step-by-step performance of the procedure, including test calculations & interpretation of results 4. Preparation of slides, solutions, calibrators, controls, reagents, stains, & other materials used in testing 5. Limitations in methodology, including interfering substances Laboratory Operations Review 61 10. System for entering results in patient record & reporting (including protocol for critical values) 14. Copies of procedures must be retained for 2 yr after discontinuance & must include dates of initial use & discontinuance. Restriction of access to information to those who have authorization and a need to know. Unauthorized disclosure of medical information could lead to charges of breach of confidentiality or invasion of privacy. Consent for a medical procedure given by patient after procedure & possible risks have been explained. Each person handling specimen must sign chain-of-custody form that accompanies specimen & documents custody of specimen at all times. Fluorometry Atoms absorb light of specific wavelength & emit light of longer wavelength (lower energy). Concentration determined by peak height ratio (height of analyte peak/height of internal standard peak). Determines osmolality (measurement of # of dissolved particles in solution, irrespective of molecular weight, size, density, or type) based on freezing-point depression. Anions move to positively charged pole (anode); cations to negatively charged pole (cathode). Some analyzers have short sample & clot detection Usually by syringes, pumps, or pressurized reagent bottles. May be calculated from Friedewald formula (if triglycerides not >400 mg/dL) or measured by direct homogeneous assays. Strict control of glucose & blood pressure can prevent progression to end-stage renal disease. Risk of intrauterine death or neonatal complications (macrosomia, hypoglycemia, hypocalcemia, polycythemia, hyperbilirubinemia). Fast of at least 8 hr 75-g glucose load Fast of at least 8 hr; 75-g glucose load None; fasting not required Only for Dx of gestational diabetes mellitus. Should be performed using method certified by National Glycohemoglobin Standardization Program. Osteoporosis, dislocated lenses in eye, mental retardation, thromboembolic events. Causes gamma region to be cathodic to point of application Must be concentrated first because of low protein concentration. Bence Jones proteins migrate to gamma region in urine electrophoresis Must be concentrated first because of low protein concentration. Can cause muscle weakness, paralysis, breathing problems, cardiac arrhythmia, death. Increase of 10єC doubles rate of rxn until around 40є50єC; then denaturation of enzyme may occur.
Gene expression profiling is being used to study the metastatic process with the goal of identifying signatures characteristic of primary tumors that have a high propensity to metastasize arrhythmia overview purchase generic nifedipine on-line, leading to a more rational basis for the use of adjuvant chemotherapy blood pressure medication night sweats cheap 20mg nifedipine overnight delivery. Bone metastases are extremely painful, cause fractures of weight-bearing bones, can lead to hypercalcemia, and are a major cause of morbidity for cancer patients. One example is multiple myeloma, where tumor cell-stromal cell interactions activate osteoclasts and inhibit osteoblasts, leading to the development of multiple lytic bone lesions. Bisphosphonates are also effective inhibitors of osteoclast function that are used in the treatment of cancer patients with bone metastases. Important changes in gene expression are mediated by the Snail and Twist family of transcriptional repressors (whose expression is induced by the oncogenic pathways), leading to reduced expression of E-cadherin, a key component of adherens junctions between epithelial cells. This, in conjunction with upregulation of N-cadherin, a change in the pattern of expression of integrins (which mediate cell-extracellular matrix associations that are important for cell motility), and a switch in intermediate filament expression from cytokeratin to vimentin, results in the phenotypic change from adherent highly organized epithelial cells to motile and invasive cells with a fibroblast or mesenchymal morphology. Host stromal cells, including tumor-associated fibroblasts and macrophages, play an important role in modulating tumor cell behavior through secretion of growth factors and proangiogenic cytokines, and matrix metalloproteinases that degrade the basement membrane. In normal tissues (left), homeostasis is maintained by asymmetric division of stem cells leading to one progeny cell that will differentiate and one cell that will maintain the stem cell pool. This occurs within highly specific niches unique to each tissue, such as in close apposition to osteoblasts in bone marrow or at the base of crypts in the colon. Here, paracrine signals from stromal cells, such as sonic hedgehog or Notchligands, as well as upregulation of -catenin and telomerase, help to maintain stem cell features of unlimited self-renewal while preventing differentiation or cell death. This occurs in part through upregulation of the transcriptional repressor Bmi-1 and inhibition of the p16Ink4a/Arf and p53 pathways. Daughter cells leave the stem cells niche and enter a proliferative phase (referred to as transit-amplifying cells) for a specified number of cell divisions, during which time a developmental program is activated, eventually giving rise to fully differentiated cells that have lost proliferative potential. Recent evidence has led to the hypothesis that cancers harbor stem cells that make up a small fraction. These cells share several features with normal stem cells, including an undifferentiated phenotype, unlimited self-renewal potential, and a capacity for some degree of differentiation; however, due to initiating mutations (mutations are indicated by lightning bolts), they are no longer regulated by environmental cues. The cancer stem cell pool is expanded, and rapidly proliferating progeny, through additional mutations, may attain stem cell properties, although most of this population is thought to have a limited proliferative capacity. Differentiation programs are dysfunctional due to reprogramming of the pattern of gene transcription by oncogenic signaling pathways. Within the cancer transit-amplifying population, genomic instability generates aneuploidy and clonal heterogeneity as cells attain a fully malignant phenotype with metastatic potential. The cancer stem cell hypothesis has led to the idea that current cancer therapies may be effective at killing the bulk of tumor cells but do not kill tumor stem cells, leading to a regrowth of tumors that is manifested as tumor recurrence or disease progression. Research is in progress to identify unique molecular features of cancer stem cells that can lead to their direct targeting by novel therapeutic agents. Cancer Cell Biology and Angiogenesis transit amplifying population, and failure of apoptosis pathways. Implicit in the cancer stem cell hypothesis is the idea that failure to cure most human cancers is due to the fact that current therapeutic agents do not kill the stem cells. If cancer stem cells can be identified and isolated, then aberrant signaling pathways that distinguish these cells from normal tissue stem cells can be identified and targeted. Oncologists eagerly await a new class of agent that may directly attack the cells that drive tumor growth. In such cases, targeted inhibition of the pathway can lead to specific killing of the cancer cells. However, targeting defects in tumor-suppressor genes has been much more difficult because the target of the mutation is often deleted. However, identifying genes that have a synthetic lethal relationship to tumorsuppressor pathways may allow targeting of proteins required uniquely by the tumor cells. Conceptually, this provides a framework for genetic screens to identify other synthetic lethal combinations involving known tumorsuppressor genes, and development of novel therapeutic agents to target dependent pathways. This list will expand to include inhibitors of pathways currently under investigation and those yet to be discovered, yielding novel therapeutics with greater efficacy with less toxicity.
Order cheap nifedipine line. Concerns with Low Blood Pressure.